Tuesday, May 10, 2011
Blog # 13: What was the most interesting about this week's dissections?
I found the dissection of the crayfish very interesting, I never really found the differences between a crayfish and a lobster until the dissection. I got to study the external and internal parts of the crayfish. While looking and observing the external parts of a crayfish I finally realized the difference between a crayfish and a lobster. The crayfish is more smaller in size, its color is more duller, and the size of claw differs. As for a lobster its bigger, has a more brighter color, and has a bigger claw. I really learned something from this weeks dissection and it was very interesting.
Blog #12: What surprised you from the worm's dissection?
Blog #11: Get a picture of alternation of generations put it in your blog and explain how it relates to plants.
Alternation of generations is a term describing the life cycle of plants. All plants meet a life cycle that takes them through both haploid and diploid generations. The multicellular diploid plant structure is called the sporophyte, which produces spores through meiotic division. The multicellular haploid plant structure is called the gametophyte, which is formed from the spore and give rise to the haploid gametes. The fluctuation between these diploid and haploid stages that occurs in plants is called the alternation of generations. The way in which the alternation of generations occurs in plants depends on the type of plant. In bryophytes, the dominant generation is haploid, so that the gametophyte comprises what we think of as the main plant. The opposite is true for tracheophytes, in which the diploid generation is dominant and the sporophyte comprises the main plant.
Blog #10: Why is dissection an important part of a biology curriculum? Which animals and/or plants should be included in biological studies?
Dissection is important because it gives the interest of studying biology. The practice of dissecting animals is an arguable topic with people thinking negative opinions towards it. These animals are killed for the purpose of teaching students more about how living things work, but with new computer technology there are more opportunities to learn without the killing of animals. Animal dissection is an important element in learning how living things tick, but it doesn’t have to involve the slaughter of animals. With computer programs students can now receive the education without interacting with a dead animal. This eliminates the need to kill millions of animals every year. More school systems are adopting the virtual dissection programs as an alternative to real dissection. I would say that people should study or dissect the marine plankton animals. It would be interesting to see the internal part of a plankton.
Blog #9:Define the different forms of community interaction: competition, commensalism, mutualism, predation, parasitism Give an example and a picture for each
Competition
Competition is an interaction between species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. This means that there is competition within the two species in survival for food, water, territory, or sunlight. For example, a smaller tree will receive less sunlight than an adjacent tree which is larger than it in a rainforest. The larger tree is competing with the smaller one for the same sunlight, thus competition.
Commensalism
Competition is an interaction between species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. This means that there is competition within the two species in survival for food, water, territory, or sunlight. For example, a smaller tree will receive less sunlight than an adjacent tree which is larger than it in a rainforest. The larger tree is competing with the smaller one for the same sunlight, thus competition.
Commensalism
Commensalism is a class of relationship between two organisms where one organism benefits but the other is neutral, there is no harm or benefit. An example of commensalism is a flatworm attaching to the horsecrab and eating the crab's food while the crab is not affected.
Mutualism
Predation
Predation is described as a biological interaction where a predator (an organism that is hunting) feeds on its prey (the organism that is attacked). Predators may or may not kill their prey prior to feeding on them, but the act of predation always results in the death of its prey and the eventual absorption of the prey's tissue through consumption. An example of predation is a lion and a zebra. The lion hunts the zebra in order for it to feed on.
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. An example of parasitism is when a flea harms their host, such as a dog, by biting their skin, sucking their blood, and causing them to itch. The flea, in turn, get food and a warm home.
Mutualism is the way two organisms biologically interact where each individual derives a fitness benefit. In other words, it is where two species are both benefited. An example of mutualism is the nectar-producing plants and its pollinators. While the pollinators (such as bees, butterflies, etc) help to pollinate the plant for reproduction, the plants also provide its pollinators with nectar as food, thus both sides benefit.
Predation
Predation is described as a biological interaction where a predator (an organism that is hunting) feeds on its prey (the organism that is attacked). Predators may or may not kill their prey prior to feeding on them, but the act of predation always results in the death of its prey and the eventual absorption of the prey's tissue through consumption. An example of predation is a lion and a zebra. The lion hunts the zebra in order for it to feed on.
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. An example of parasitism is when a flea harms their host, such as a dog, by biting their skin, sucking their blood, and causing them to itch. The flea, in turn, get food and a warm home.
Monday, May 2, 2011
Blog #8: Your choice talk about something you learned or ask a question about something that is confusing you
Well so far throughout 2nd semester, I've learned alot of things but above them all, the two main topics I enjoyed learning about were about evolution and dissections.
I've learned that evolution is the change over time and that the inherited traits from an ancestor is passed down from the generation to the next. Evolution may occur when there is variation of inherited traits within a population. Evolution has led to the diversification of all living organisms. I found the evolution topic interesting because I learned about the ancestors of every living organism and how their traits are passed down into the organisms that live today.
I've learned that evolution is the change over time and that the inherited traits from an ancestor is passed down from the generation to the next. Evolution may occur when there is variation of inherited traits within a population. Evolution has led to the diversification of all living organisms. I found the evolution topic interesting because I learned about the ancestors of every living organism and how their traits are passed down into the organisms that live today.
The second thing I learned was dissection within living things. Dissection is the process of disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and as an aid to discerning the functions and relationships of its components. In biology we mostly dissected plants or animals such as, a worm. We observed the worm's insides and learned where they are found and how they work. I find dissection an interesting thing to learn.
Blog #7:Compare and contrast two biomes describe them in detail include pictures of plants and animals you are liklely to see
One biome is the tropical rain forest biome. The tropical rain forest is a forest of tall trees in a region of year-round warmth. There are so many different kinds of plants in a rainforest , scientists don't even know them all yet. Theses are some plants you may see in a tropical rainforest: trees, air plants, and bromeliads. Billions of animals, birds, and insects live in the tropical rainforest. Some are: bats, turtles, salamanders, macaws, and snails.
Another biome is the desert. The desert is a place on earth that is characterized by little vegetation and rain. They are made up of sand or rocks and gravel. There are some plants that are able to survive in the desert, these plants have to adjust to the hot days and to the cold nights. These are some plants you may see in the desert: cacti, and the joshua tree, which is similar to the cacti. There are many animals found in the desert but most of them come out at night, and during the day they hide under sand or rocks to keep cool. Here are some animals that live in the desert: the jack rabbit, and camels.
Tuesday, March 29, 2011
Blog #6: Which level of a food pyramid is the most important? Support your answer
I think that dairy is the most important level because it gives you your calcium. Calcium makes our bones strong and healthy as well as our teeth. Milk or other dairy products are the richest sources of calcium which is why you should drink it everyday. They also contain other vitamins and minerals, as well as protein. Some dairy products can be high in fat, but there are plenty of lower fat options you can choose, or you could have just a small amount of the high-fat varieties. Other sources of calcium include fortified breakfast cereal, soy beans, tofu, soy drinks with added calcium, dried figs, okra, curly kale, rice pudding and baked beans.
Blog #5:There have been 5 major extinction events throughout history, are humans impacting the 6th? Why or why not?
Thursday, February 24, 2011
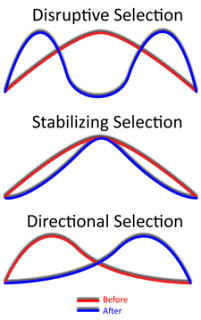
Blog #4:Describe the three types of selection: directional, stabilizing and disruptive and give an example of each in your own words.
Directional selection is a function of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. In directional selection, the different allele increases in frequency independently of its dominance relative to other alleles. Directional selection stands in opposite to balancing selection where selection may favor multiple alleles, and is the same as purifying selection which removes harmful mutations from a population. An example can be found in the breeding of the greyhound dog. Early breeders were interested in dog with the greatest speed. They carefully selected from a group of hounds those who ran the fastest. From their offspring, the greyhound breeders again selected those dogs who ran the fastest. By continuing this selection for those dogs who ran faster than most of the hound dog population, they gradually produced a dog who could run up to 64km/h (40mph).
Stabilizing selection is also a type of natural selection where genetic diversity decreases as the population stabilizes on a particular trait value. This is probably the most common mechanism of action for natural selection. Stabilizing selection commonly uses negative selection to select against extreme values of the character. Stabilizing selection acts to prevent divergence of form and function. An example of stabilizing selection is human birth weight. Babies of low weight lose heat more quickly and get ill from infectious diseases easily, but babies with large body weight are difficult to deliver through the pelvis.
Disruptive selection favors the extremes of a range of selection. Disruptive selection refers to natural selection that favors phenotypic extremes. An example of this is a population of seed-eating birds with beaks that range in size, so that big beaks are best adapted to eating big seeds, small beaks are best adapted to small seeds, and medium beaks are best adapted to medium seeds. Now suppose that the source of medium seeds goes extinct it looses its food source, selection favors the big and small beaks.
Blog #3: Explain what microevolution is? What are the three ways that variation occurs?
Variation can occur three different ways. Variation can occur when all the organisms produce more offspring then one can survive to adulthood and reproduce, many of these offspring will die without reproduction. Another way that variation can occur is when the variation is heritable, if it's in the parents it's passed on to the offspring. A third way that variation can occur is by an absence of mutation.
Blog #2: Why is fossil record hard to interpret?
The fossil record is hard to interpret because paleontologists sometimes they find the remains of an entire organism or sometimes the find parts of a it. It's hard to explain a fossil because it could come in different shapes and sizes. Sometimes it can be the sand or the layers of dirt that covers the fossil that makes it so hard to interpret. Paleontologist have to be careful not to break the fossil when interpreting it. It is very hard to interpret a fossil when it's a small animal because the bones of the fossils are so small. But when interpreting a large animal, it takes long to explain it but its still very hard. They often have to build an extinct species from a few fossil bits- bones, shells, leaves or pollen. When paleontologists study a fossil they look for related similarities and differences between the fossil and living organisms. Paleontologists also have to determine the age of the fossil, which is really important.
Monday, February 7, 2011
Blog #1: Why is evolution a theory not a law?
A theory is more of an explanation. A law is a pattern that natural phenomena follow. So they're two different things. A law is great for predicting events, because we expect the events to follow the pattern. But the law won't explain why events follow the pattern. For that we need a theory. Both theories and laws can turn out to be wrong, and must be tested by considering what evidence we should find if the theory or law were false, and then looking for such evidence. A law must be confirmed and broadly agreed upon through the process of inductive reasoning. A theory is a well-supported body of interconnected statements that explains observations and can be used to make testable predictions. Evolution is not a law because evolution describes the mechanisms of how and why organisms change over time. In all honesty, no scientists disbelieve evolution at this point. There is disagreement on some of the details of the theory – the details of the how and why – but not the big questions that things evolve or even the general ideas of how and why.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)